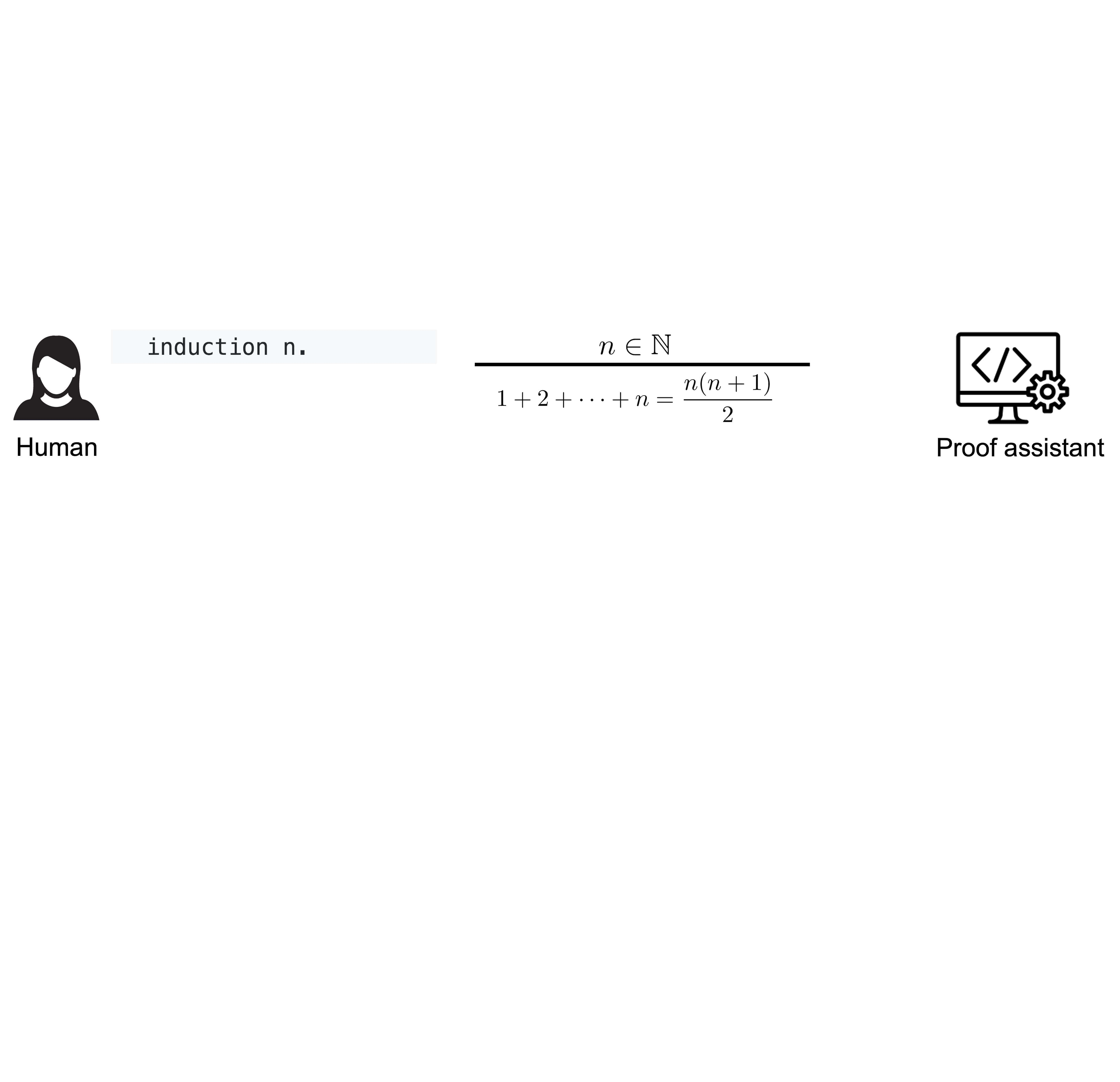
|
杨凯峪 / kaiyuy [at] alumni [dot] princeton [dot] edu / CV / Google Scholar / GitHub I'm leading a research team on verifiable AI at MiroMind.
|

|
|
I aim to build verifiable AI that produces results whose correctness can be trusted without labor-intensive human checking. Today’s AI can generate code, proofs, and arguments at scale, but verifying their correctness often takes more time than doing the work manually. I address this bottleneck by developing AI capable of formal reasoning. Grounded in formal systems such as Lean, AI can generate solutions paired with concise specifications and machine-checkable proofs. Humans then verify only the specification, while the formal system guarantees correctness. This shifts the role of humans from tedious verification to high-level guidance, enabling faster and more reliable progress in AI-accelerated mathematics, software development, and scientific discovery. My research spans AI for formal theorem proving (LeanDojo, CoqGym, Goedel-Prover), autoformalization (LeanEuclid), and applications in formal mathematics and verification, including solving competition-level problems (LIPS), assisting mathematicians (Lean Copilot, Lean Finder), and generating verifiable code (Verina). Together, these efforts point towards integrated AI systems that reason rigorously across informal and formal domains and produce verifiable solutions with guaranteed correctness. |

|
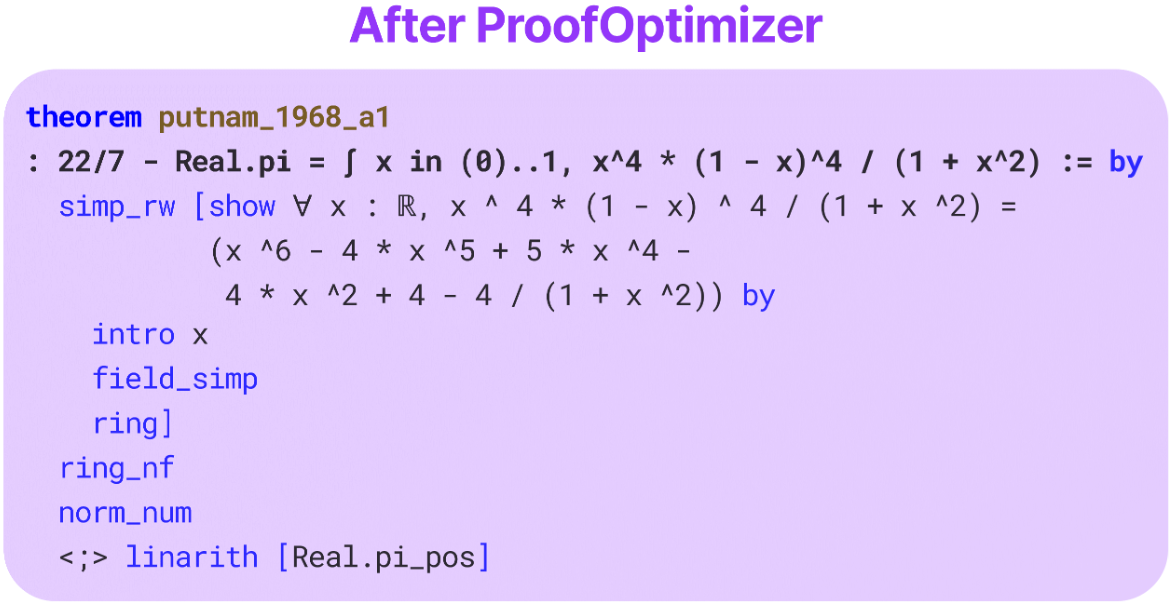
Alex Gu, Bartosz Piotrowski, Fabian Gloeckle, Kaiyu Yang, Aram Markosyan International Conference on Learning Representations (ICLR), 2026 arXiv / project / demo LLMs trained with reinforcement learning often produce formal proofs that are correct but excessively long and opaque. We introduce ProofOptimizer, a system that automatically shortens and cleans up these proofs while preserving correctness. It reduces proof length by up to 87% on MiniF2F and 57% on PutnamBench, making formal proofs more readable and revealing clearer mathematical insights. |

|
Jialin Lu, Kye Emond, Kaiyu Yang, Swarat Chaudhuri, Weiran Sun, Wuyang Chen International Conference on Learning Representations (ICLR), 2026 arXiv / project We present Lean Finder, a semantic search engine for Lean and mathlib that understands and aligns with the intents of mathematicians. |
|
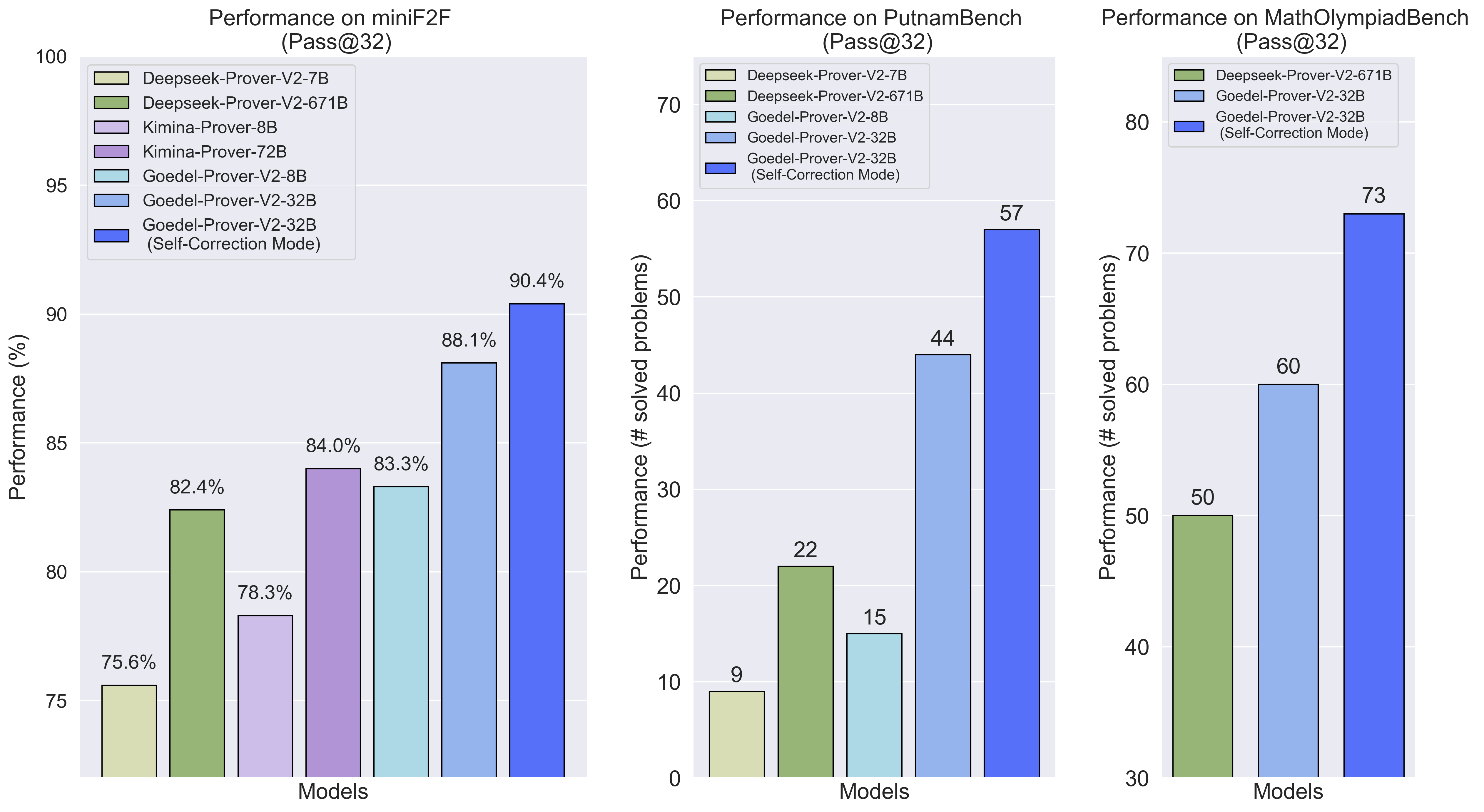
Yong Lin*, Shange Tang*, Bohan Lyu*, Ziran Yang*, Jui-Hui Chung*, Haoyu Zhao*, Lai Jiang*, Yihan Geng*, Jiawei Ge, Jingruo Sun, Jiayun Wu, Jiri Gesi, David Acuna, Kaiyu Yang, Hongzhou Lin*, Yejin Choi, Danqi Chen, Sanjeev Arora, Chi Jin* International Conference on Learning Representations (ICLR), 2026 arXiv / project / code Our Goedel-Prover-V2 doubled the SOTA Pass@32 performance on PutnamBench with a 20x smaller model. |
|
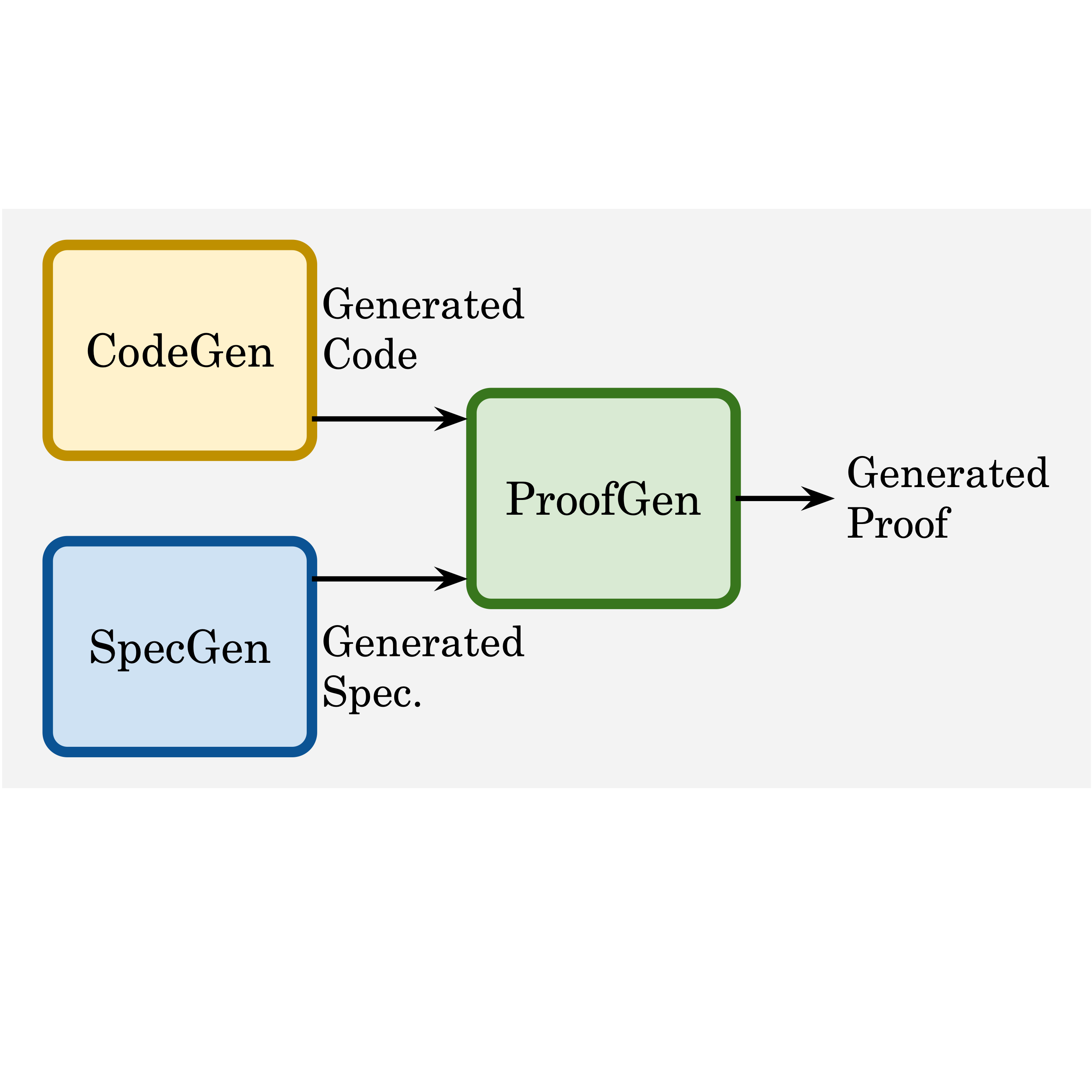
Zhe Ye, Zhengxu Yan, Jingxuan He, Timothe Kasriel, Kaiyu Yang, Dawn Song International Conference on Learning Representations (ICLR), 2026 arXiv / project / data / code We introduce Verina (Verifiable Code Generation Arena), a high-quality benchmark for verifiable code generation (joint generation of code, specifications, and proofs) in Lean |

|
Kaiyu Yang, Gabriel Poesia, Jingxuan He, Wenda Li, Kristin Lauter, Swarat Chaudhuri, Dawn Song International Conference on Machine Learning (ICML), Position Papers Track, 2025, Spotlight A separate version accepted to Communications of the ACM arXiv / CACM This position paper advocates for formal mathematical reasoning, i.e., mathematical reasoning grounded in formal systems such as proof assistants. It is complementary to the informal approach (training LLMs on mathematical texts) and is arguably indispensable for advancing AI4Math to the next level. |
|
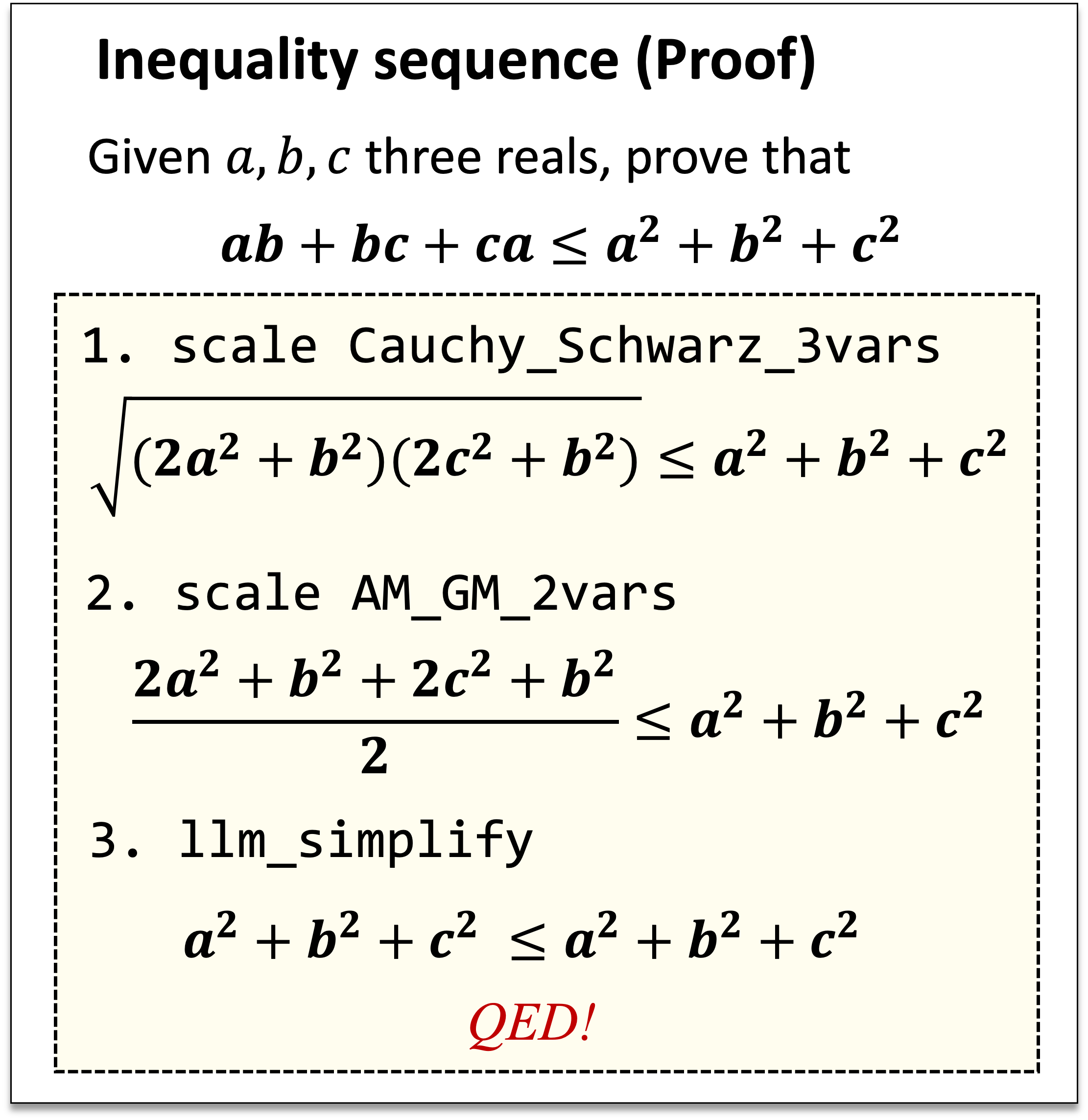
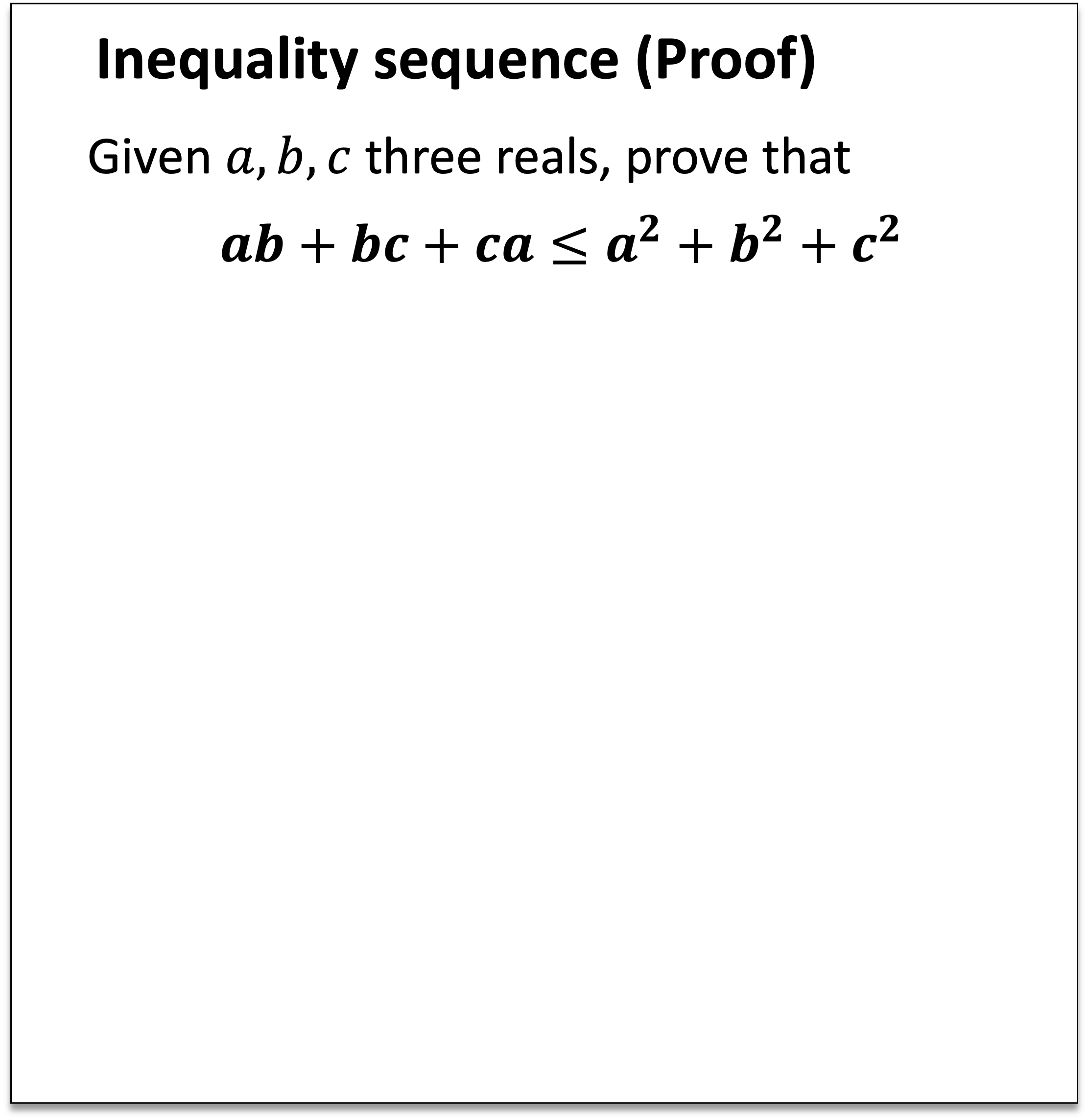
Zenan Li*, Zhaoyu Li* Wen Tang, Xian Zhang, Yuan Yao, Xujie Si, Fan Yang, Kaiyu Yang†, Xiaoxing Ma† († equal advising) International Conference on Learning Representations (ICLR), 2025 arXiv / code To prove inequalities in math competitions, we analyze and distill human techniques into scaling and rewriting, which are well-suited for symbolic methods and LLMs respectively. By integrating LLMs with domain-specific mathematical insights, our approach substantially outperforms existing methods. |
|
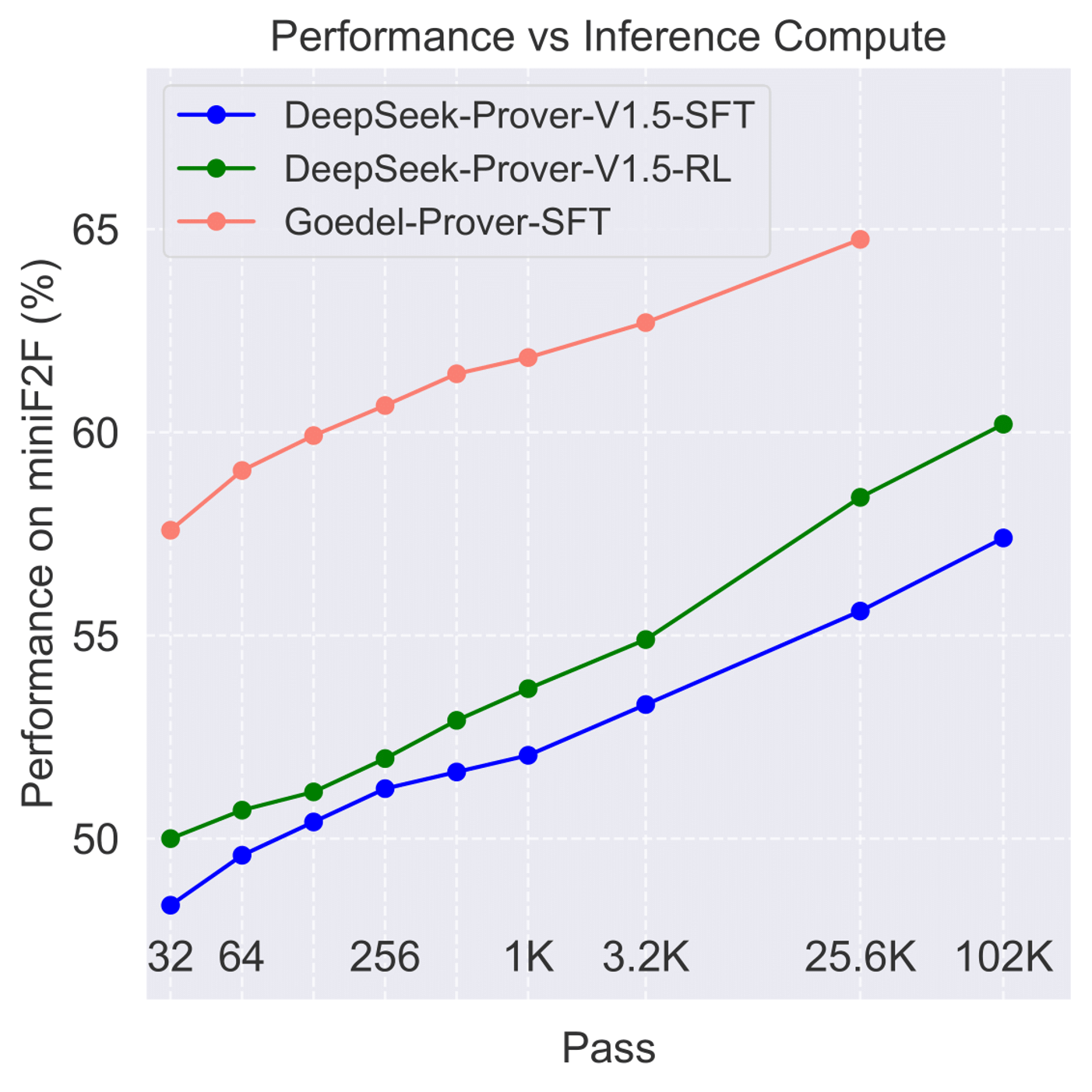
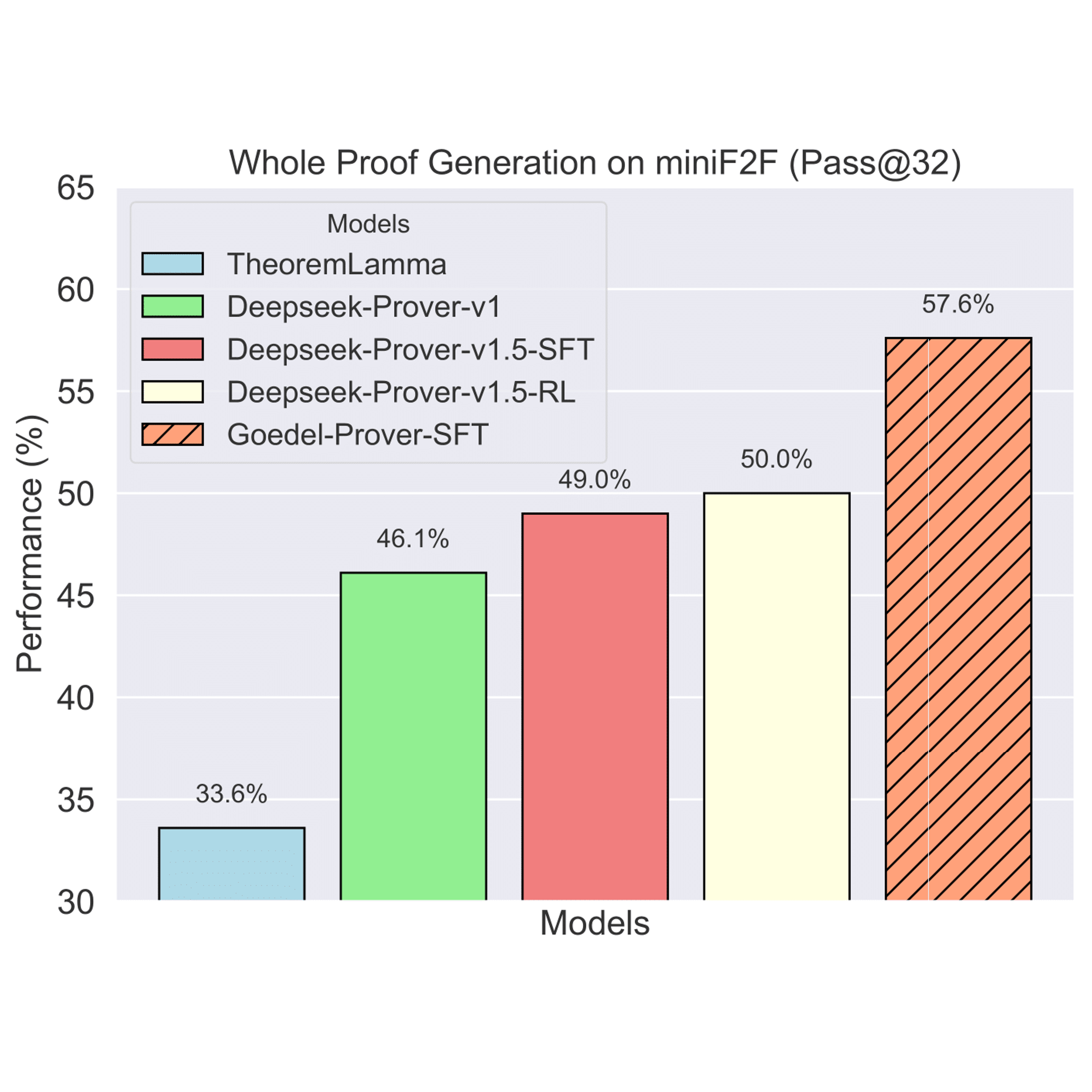
Yong Lin*, Shange Tang*, Bohan Lyu, Jiayun Wu, Hongzhou Lin, Kaiyu Yang, Jia Li, Mengzhou Xia, Danqi Chen, Sanjeev Arora, Chi Jin Conference on Language Modeling (COLM), 2025 arXiv / project / code We introduce Goedel-Prover, an open-source, state-of-the-art LLM for automated theorem proving in Lean. The key is to synthesize 1.64 million formal statements through autoformalization. |
|
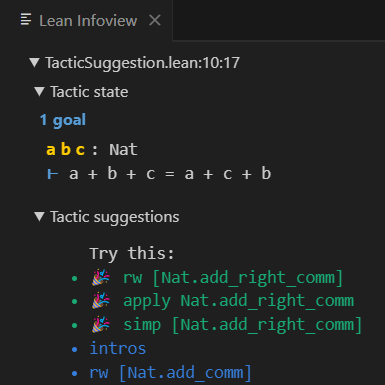
Peiyang Song, Kaiyu Yang, Anima Anandkumar International Conference on Neuro-symbolic Systems (NeuS), 2025 arXiv / code / demo / talk / media We introduce a framework for running neural network inference directly in Lean. It enables programmers to build various LLM-based proof automation tools that integrate seamlessly into the workflow of Lean users, including tools for suggesting proof steps and completing intermediate proof goals using LLMs. |
|
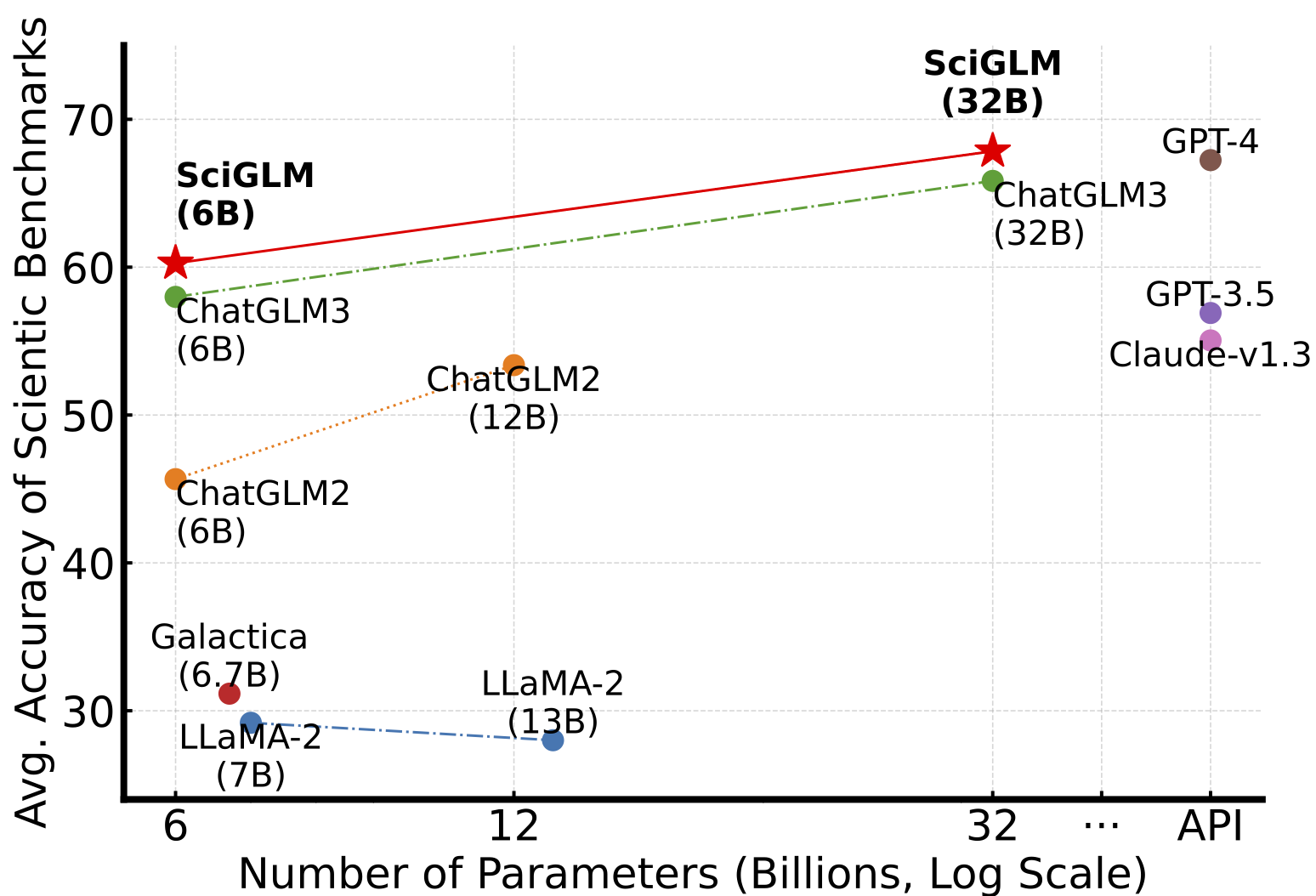
Dan Zhang, Ziniu Hu, Sining Zhoubian, Zhengxiao Du, Kaiyu Yang, Zihan Wang, Yisong Yue, Yuxiao Dong, Jie Tang Neural Information Processing Systems (NeurIPS), Datasets and Benchmarks Track, 2024 arXiv / code We curated SciInstruct, a diverse and high-quality dataset of college-level mathematics, physics, chemistry, and formal proofs. Using SciInstruct to finetune the ChatGLM family of LLMs, we introduce SciGLM, a suite of scientific language models for college-level mathematical/scientific reasoning. |
|
Zhaoyu Li, Jialiang Sun, Logan Murphy, Qidong Su, Zenan Li, Xian Zhang, Kaiyu Yang, Xujie Si Conference on Language Modeling (COLM), 2024 arXiv / code We present the first comprehensive survey of deep learning for theorem proving and autoformalization. |

|
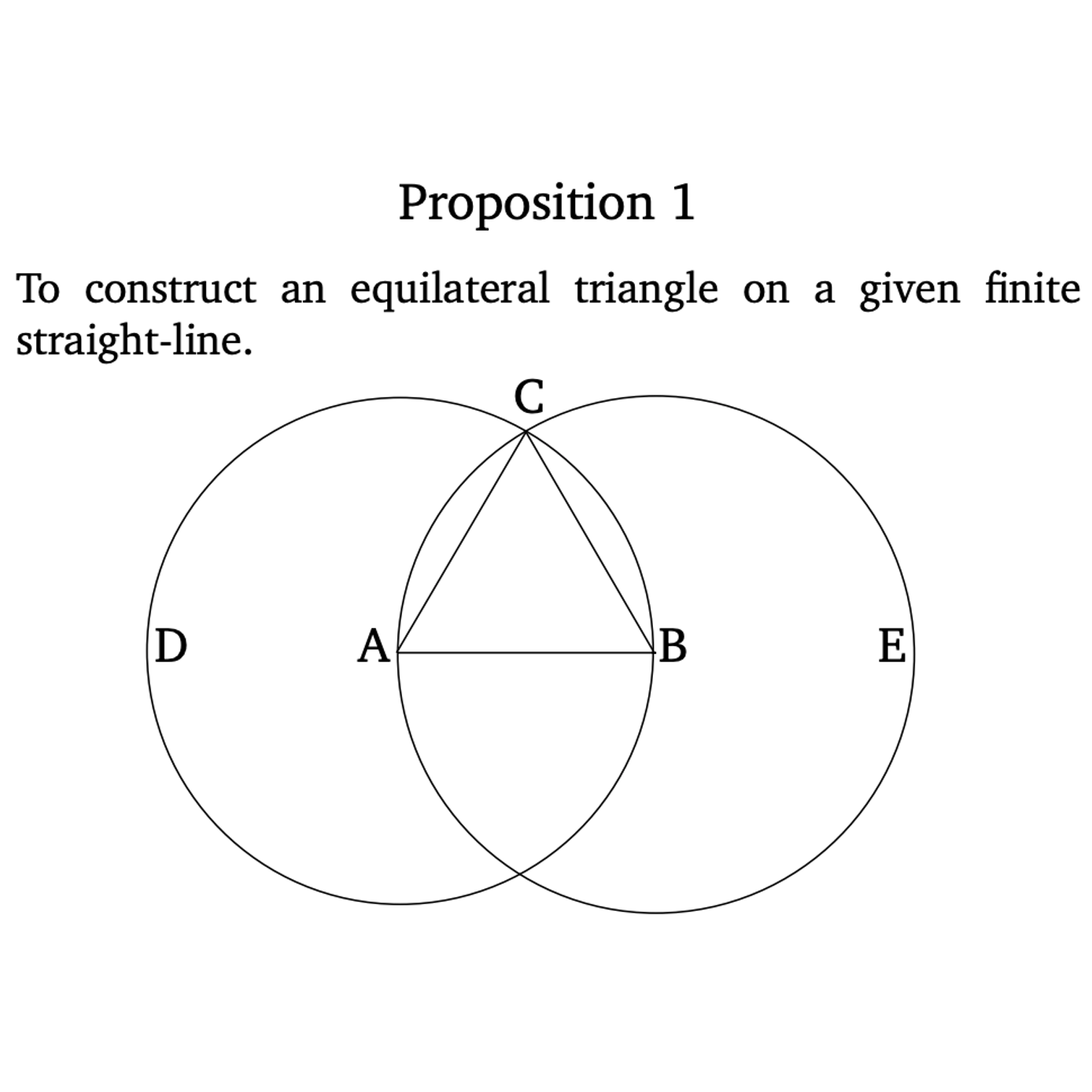
Logan Murphy*, Kaiyu Yang*, Jialiang Sun, Zhaoyu Li, Anima Anandkumar, Xujie Si (* equal contribution) International Conference on Machine Learning (ICML), 2024 arXiv / code We release LeanEuclid, a benchmark for testing autoformalization, consisting of Euclid's Elements (Book I) manually formalized in Lean. It is challenging for state-of-the-art LLMs like GPT-4V. Furthermore, the process of constructing LeanEuclid has uncovered intriguing ambiguities in Euclid's original works. |
|
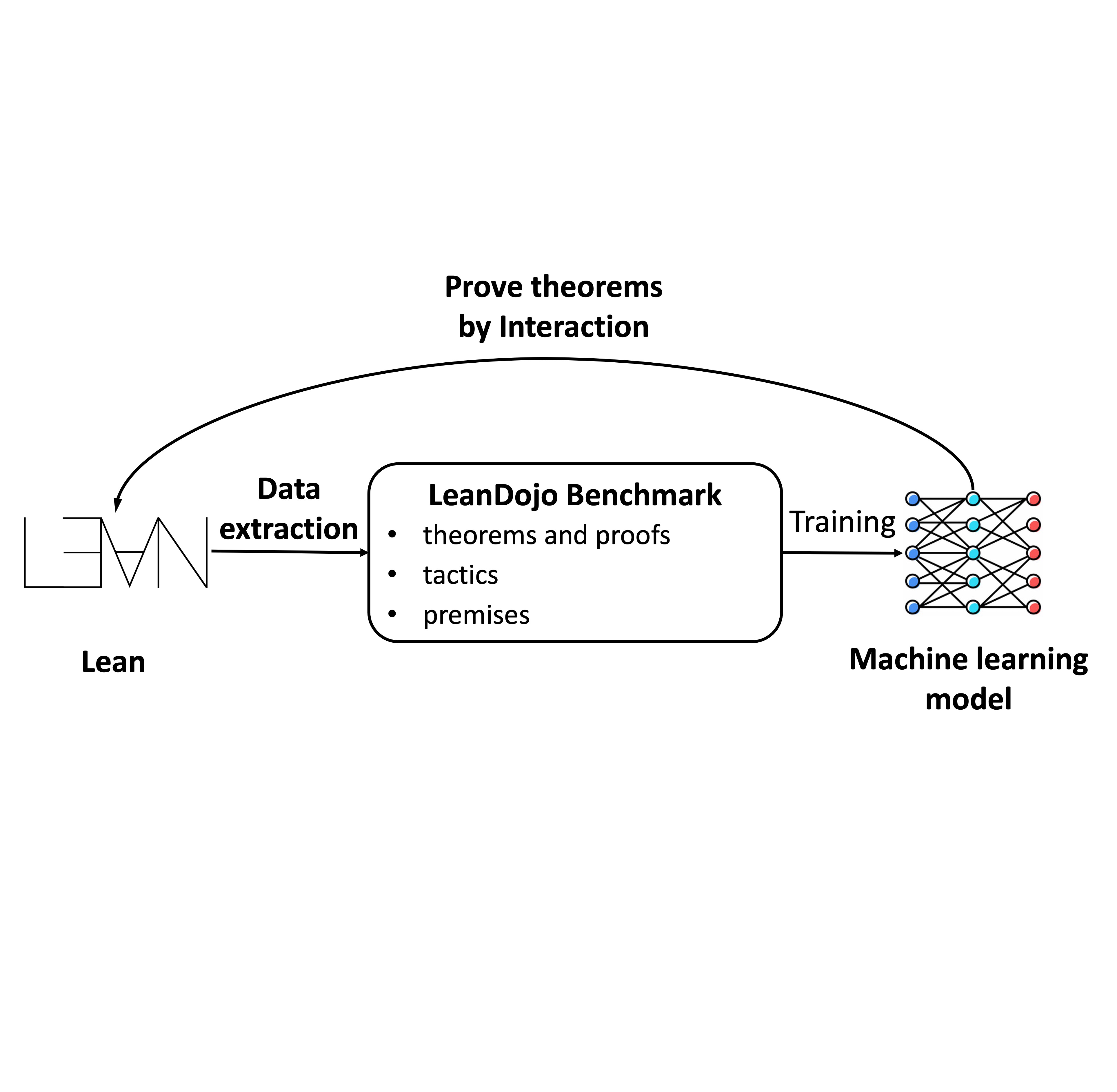
Kaiyu Yang, Aidan Swope, Alex Gu, Rahul Chalamala, Peiyang Song, Shixing Yu, Saad Godil, Ryan Prenger, Anima Anandkumar Neural Information Processing Systems (NeurIPS), Datasets and Benchmarks Track, 2023, Oral presentation arXiv / project / code / talk / slides / media Can LLMs generate mathematical proofs that can be rigorously checked? We release LeanDojo: an open-source playground consisting of toolkits, benchmarks, and models for LLMs to prove formal theorems in the Lean proof assistant. |
|
Alexander Raistrick*, Lahav Lipson*, Zeyu Ma*, Lingjie Mei, Mingzhe Wang, Yiming Zuo, Karhan Kayan, Hongyu Wen, Beining Han, Yihan Wang, Alejandro Newell, Hei Law, Ankit Goyal, Kaiyu Yang, Jia Deng Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), 2023 arXiv / project / code Data drives progress in computer vision. We introduce Infinigen: a generator of unlimited high-quality 3D data. 100% procedural, no external assets, no AI. Free and open source. |
|
|
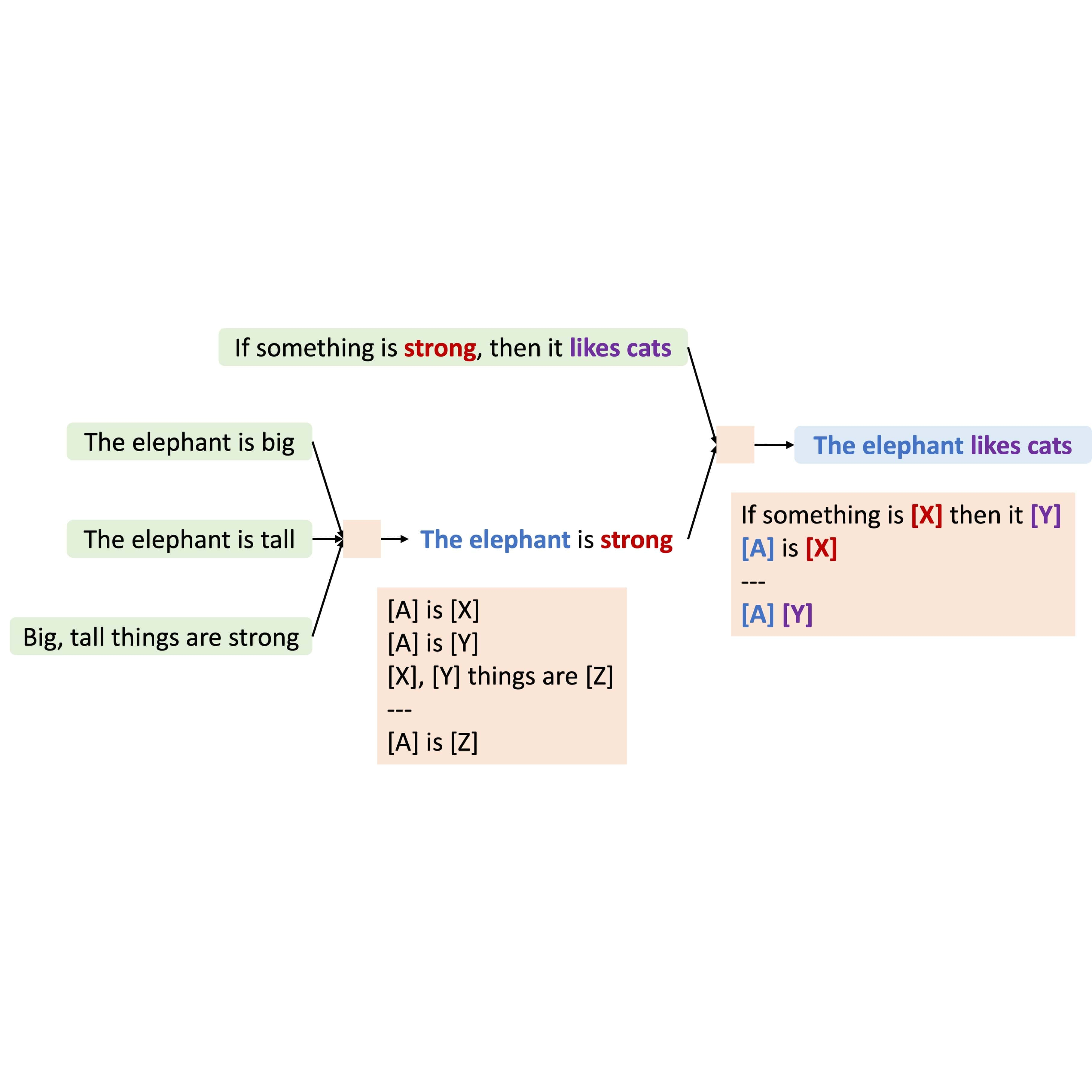
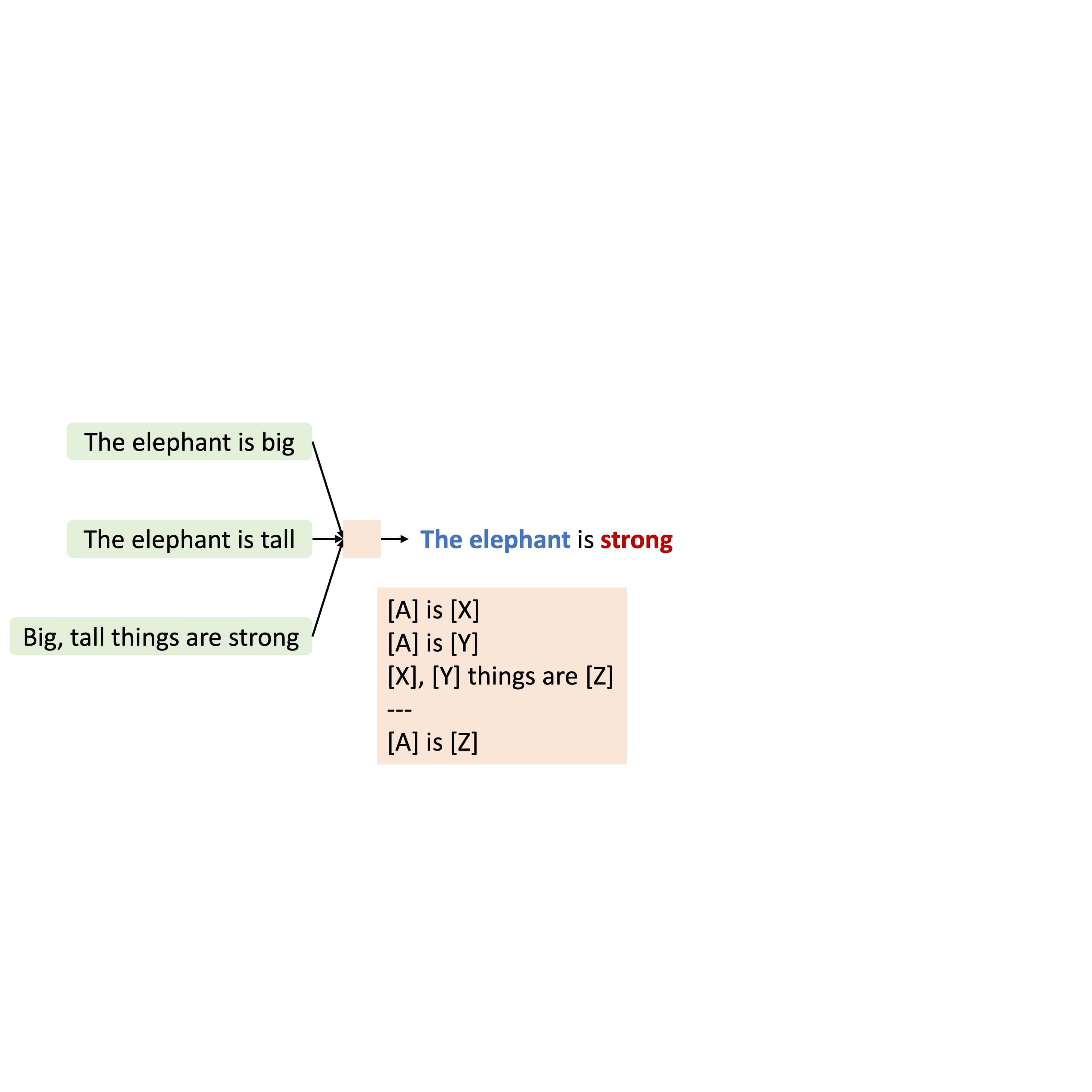
Kaiyu Yang and Jia Deng Transactions on Machine Learning Research (TMLR), 2023 arXiv / code We propose MetaQNL, a symbolic "Quasi-Natural" language that can express both formal logic and natural language. Instead of manually constructing MetaQNL rules, we propose MetaInduce: an algorithm for learning rules from data. |

|
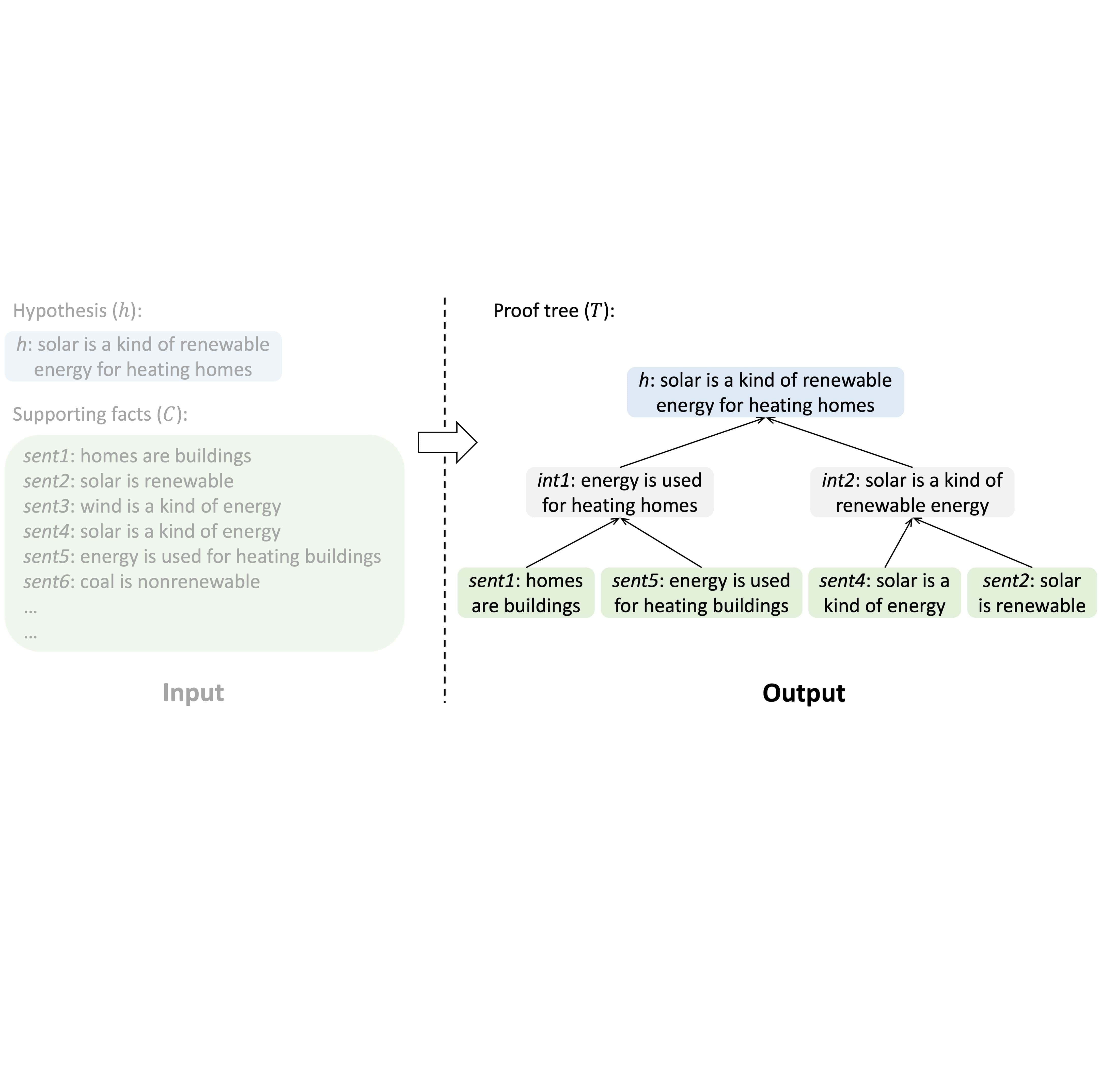
Kaiyu Yang, Jia Deng, Danqi Chen Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing (EMNLP), 2022, Oral presentation arXiv / code / slides We introduce NLProofS (Natural Language Proof Search) for multi-step logical reasoning in natural language. Given a hypothesis and a set of supporting facts, it generates a proof tree indicating how to derive the hypothesis from supporting facts. |


|
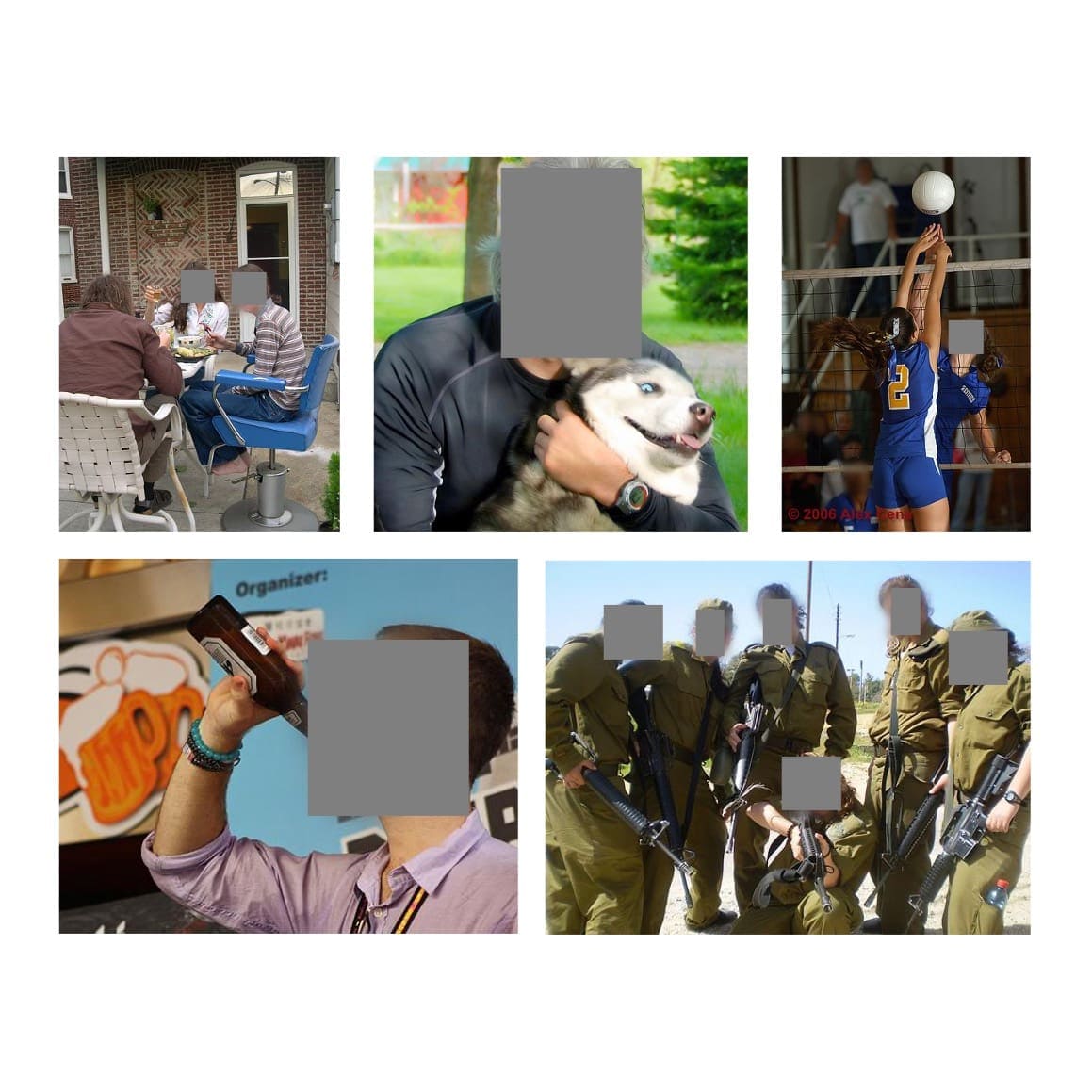
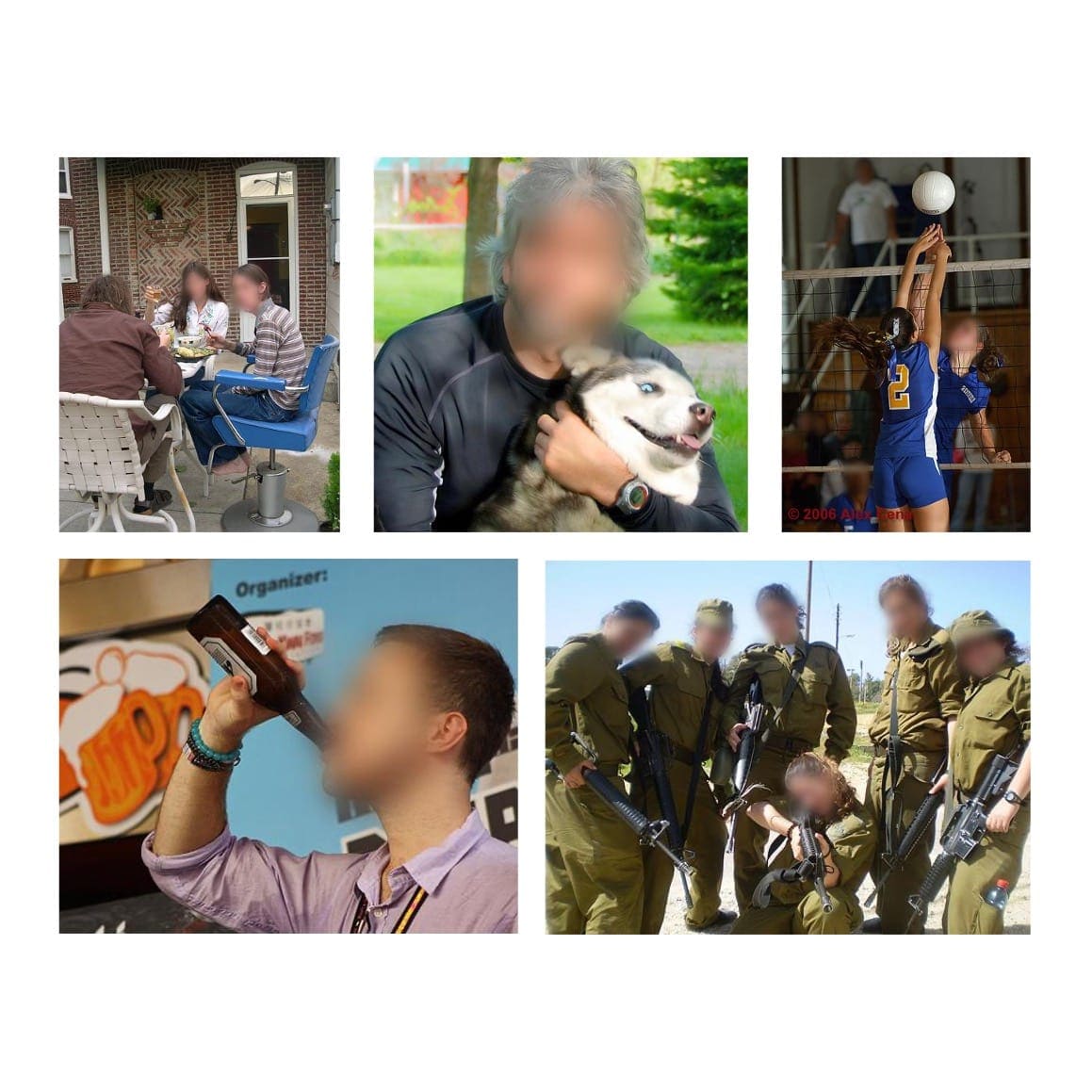
Kaiyu Yang, Jacqueline Yau, Li Fei-Fei, Jia Deng, Olga Russakovsky International Conference on Machine Learning (ICML), 2022 arXiv / code / slides / talk / project / media We annotate human faces in ImageNet and obfuscate them for privacy protection. We show that face obfuscation does not hurt image classification and transfer learning. |

|
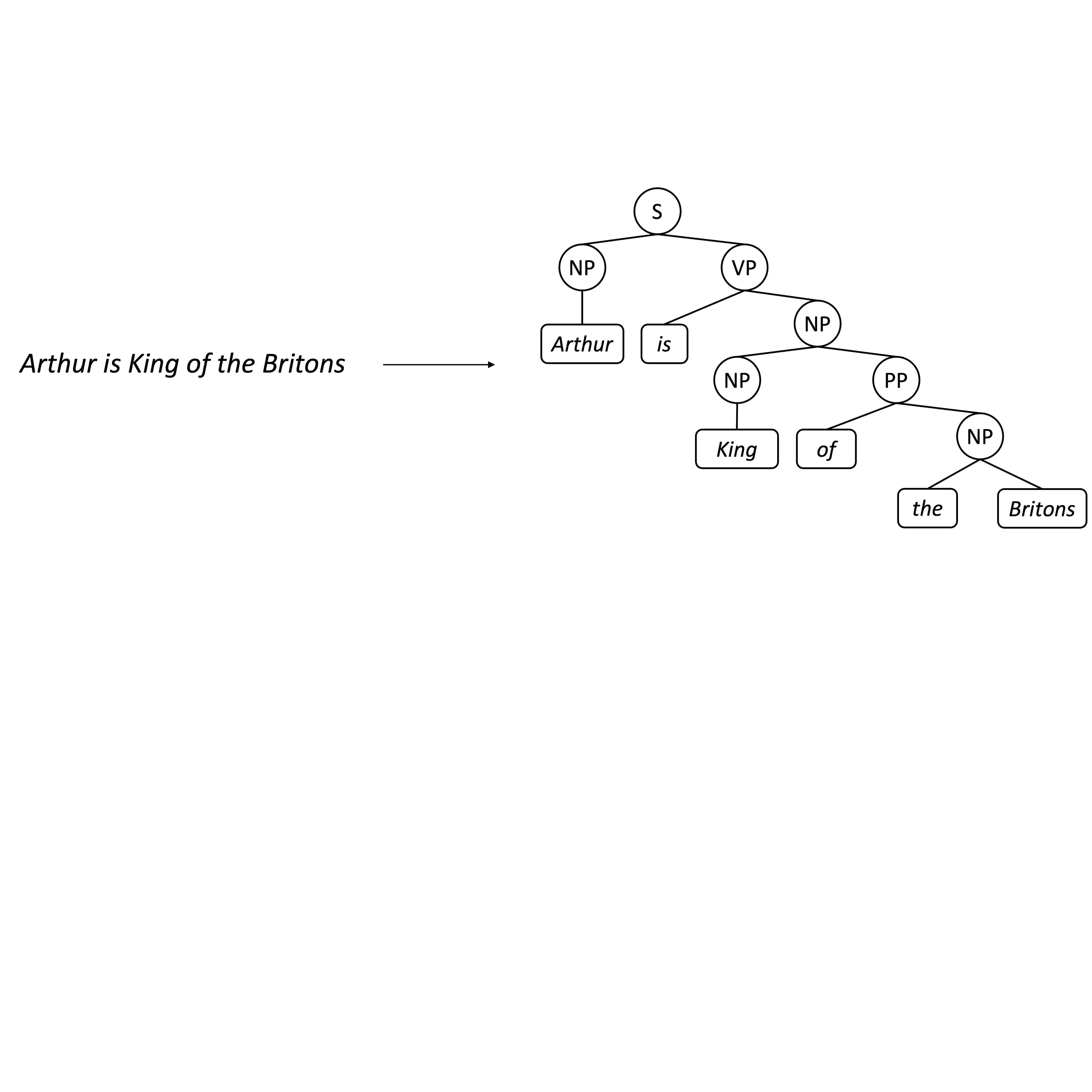
Kaiyu Yang and Jia Deng Neural Information Processing Systems (NeurIPS), 2020 arXiv / code / slides / talk We propose a novel transition-based constituency parser named Attach-Juxtapose, inspired by how humans perform parsing. |

|
Ankit Goyal, Kaiyu Yang, Dawei Yang, Jia Deng Neural Information Processing Systems (NeurIPS), 2020, Spotlight arXiv / code We propose Minimally Contrastive Data Collection: a novel crowdsourcing method for reducing dataset bias. And we use it to construct Rel3D—the first large-scale, human-annotated dataset for grounding spatial relations in 3D. |

|
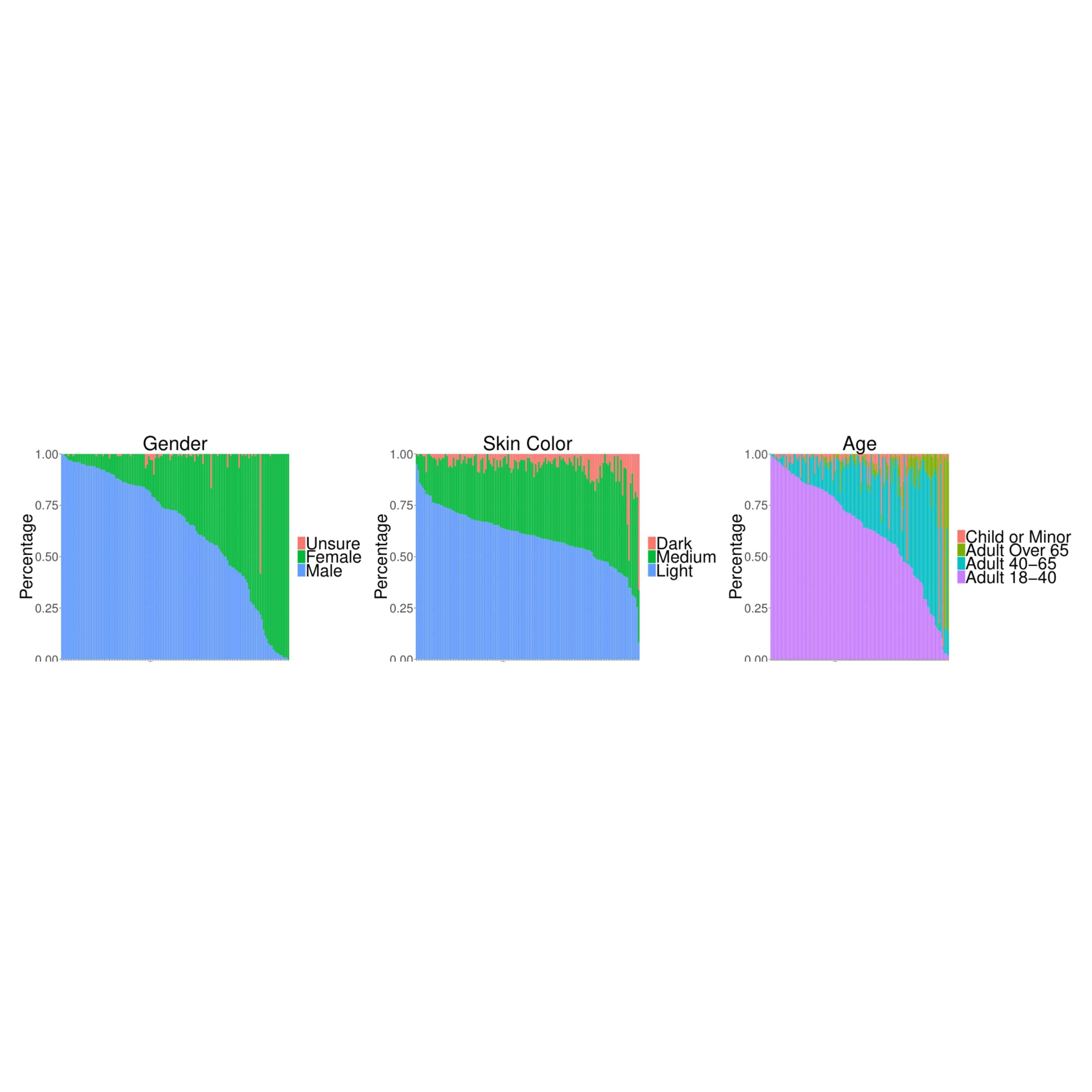
Kaiyu Yang, Klint Qinami, Li Fei-Fei, Jia Deng, Olga Russakovsky Conference on Fairness, Accountability, and Transparency (FAT*), 2020 arXiv / slides / talk / blog / media We reveal and mitigate fairness issues of ImageNet, filtering its concept vocabulary and balancing its representation of various demographic groups in images. |
|
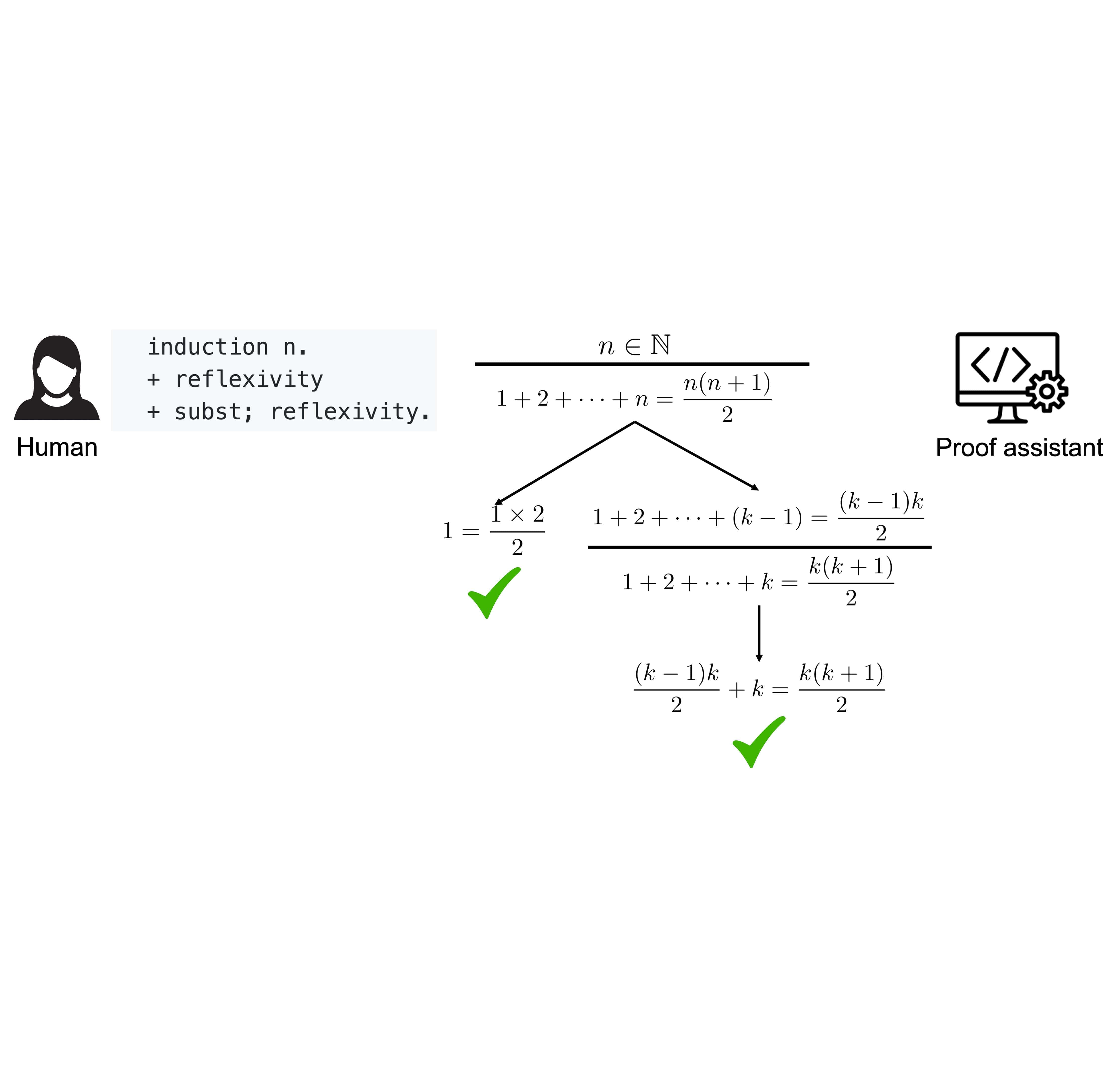
Kaiyu Yang and Jia Deng International Conference on Machine Learning (ICML), 2019 arXiv / code / slides We introduce CoqGym, one of the first and largest datasets for theorem proving in proof assistants, and ASTactic, a deep learning prover generating tactics as programs. |


|
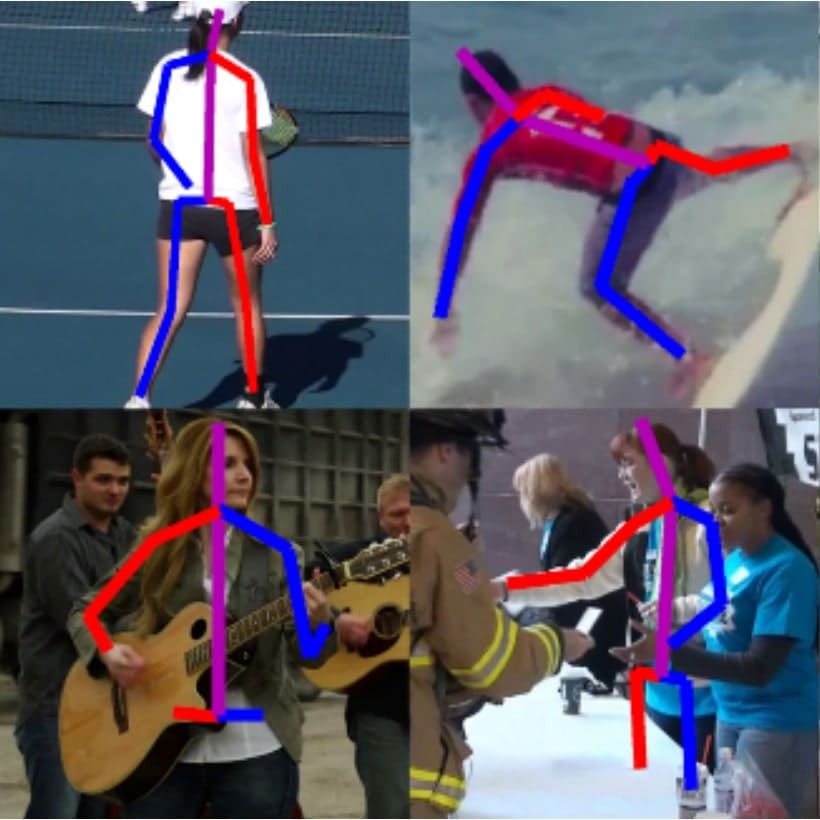
Kaiyu Yang, Olga Russakovsky, Jia Deng International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), 2019 arXiv / code We propose Adversarial Crowdsourcing to reduce dataset bias and use it to construct SpatialSense, a challenging dataset for recognizing spatial relations in images. |

|
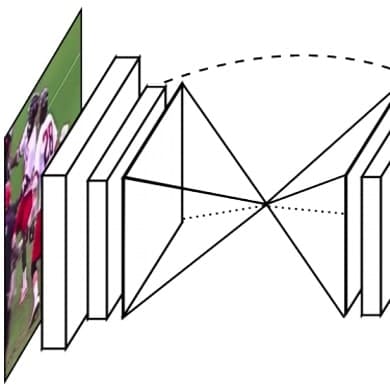
Alejandro Newell, Kaiyu Yang, Jia Deng European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), 2016 arXiv / code We introduce Stacked Hourglass Networks—one of the most popular architectures for human pose estimation, object detection, and more. |
|
I'm a core developer of the following GitHub repos: |
|
I'm a co-organizer of the following events:
|
|
My works are covered by:
|
|
I'm fortunate to have worked with many talented students and junior researchers:
|
|
|
|
Website template credit: Jon Barron |
 We're hiring
We're hiring 


